Ladies and gentlemen, let us shed some light on the fascinating world of solar-powered welding helmets! Ever wondered how these ingenious devices protect our eyes against the intense brightness of welding arcs? Well, wonder no more, as we unravel the inner workings of these helmets. By harnessing the incredible power of the sun, solar-powered welding helmets offer a unique solution to this age-old problem, ensuring both safety and convenience for welders everywhere. So, grab your protective goggles and join us on this illuminating journey as we explore the mysteries behind these remarkable pieces of equipment.
Review contents
Overview
What is a solar-powered welding helmet?
A solar-powered welding helmet is a type of protective headgear specifically designed for welders. It is equipped with advanced technology that utilizes solar power to generate electricity, which in turn powers various features of the helmet. The helmet offers crucial protection to welders by shielding their eyes and face from the intense light, heat, and sparks generated during the welding process. The solar-powered aspect of the helmet eliminates the need for batteries or external power sources, making it more convenient and cost-effective.
Why are solar-powered welding helmets popular?
Solar-powered welding helmets have gained immense popularity among welders for several reasons. Firstly, the use of solar power eliminates the need to constantly change batteries or charge the helmet, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Additionally, these helmets provide a consistent power supply, ensuring uninterrupted and reliable operation. The advanced technology used in these helmets also offers features like auto-darkening, adjustable shade levels, and quick reaction time, enhancing safety and improving the overall welding experience. Furthermore, solar-powered welding helmets contribute to a cleaner environment by minimizing the use of non-renewable energy sources.
How do solar-powered welding helmets differ from traditional welding helmets?
Solar-powered welding helmets differ from traditional welding helmets primarily in terms of power source and features. Traditional helmets typically rely on replaceable batteries, while solar-powered helmets utilize solar power to generate electricity, ensuring a continuous and self-sustainable power supply. This eliminates the need for frequent battery replacements or recharging. Solar-powered helmets also incorporate advanced technology like auto-darkening, which automatically adjusts the shade of the helmet’s lens based on the intensity of the light produced while welding. Traditional helmets usually have fixed shades that require manual adjustment. These advancements in solar-powered helmets enhance safety, visibility, and user comfort, making them a preferred choice for welders.
Solar Power Generation
Photovoltaic Cells
Solar-powered welding helmets harness the power of photovoltaic cells to generate electricity. These cells, often made from semiconductor materials like silicon, are designed to convert sunlight into electrical energy. When exposed to light, the cells absorb photons, which results in the release of electrons. This electron flow creates an electrical current that can be harvested and utilized.
Conversion of sunlight into electricity
The photovoltaic cells in solar-powered welding helmets convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This process involves the absorption of photons by the semiconductor material, which causes the release of electrons. The movement of these electrons creates an electrical current that powers the various components of the welding helmet.
Energy storage
Solar-powered welding helmets incorporate energy storage systems to ensure a consistent power supply. These systems typically use rechargeable batteries to store excess energy generated by the photovoltaic cells. During periods of low sunlight or when the welding helmet requires more power than what the cells can generate, the stored energy from the batteries is utilized. This ensures uninterrupted operation and reduces reliance on direct sunlight.
This image is property of www.euromarc.co.nz.
Auto-darkening Technology
What is auto-darkening technology?
Auto-darkening technology is a key feature in solar-powered welding helmets that automatically adjusts the shade of the helmet’s lens based on the intensity of the welding arc. It eliminates the need for manual adjustment of the shade level, providing convenience and allowing welders to maintain focus and productivity without interruptions.
Light sensors and their role
Solar-powered welding helmets are equipped with light sensors that detect the level of brightness produced by the welding arc. These sensors analyze the intensity of the light and communicate with the auto-darkening system to instantly darken the lens. This rapid response ensures that the welder’s eyes are protected from the harmful effects of the intense light produced during welding.
Adjustable shade levels
Solar-powered welding helmets offer the flexibility to adjust the shade level according to the specific requirements of different welding tasks. The shade level determines the level of darkness the lens provides, with higher shade numbers providing greater protection from intense light. This adjustable feature allows welders to customize their visibility and optimize their comfort and safety while working.
Reaction time
The reaction time of the auto-darkening technology in solar-powered welding helmets refers to the speed at which the lens transitions from a clear state to a darkened state. Modern helmets have significantly reduced reaction times, with some models boasting transition times as fast as 1/20,000th of a second. The quick response ensures that the welder’s eyes are shielded from the intense light almost instantaneously, minimizing the risk of eye damage caused by prolonged exposure.
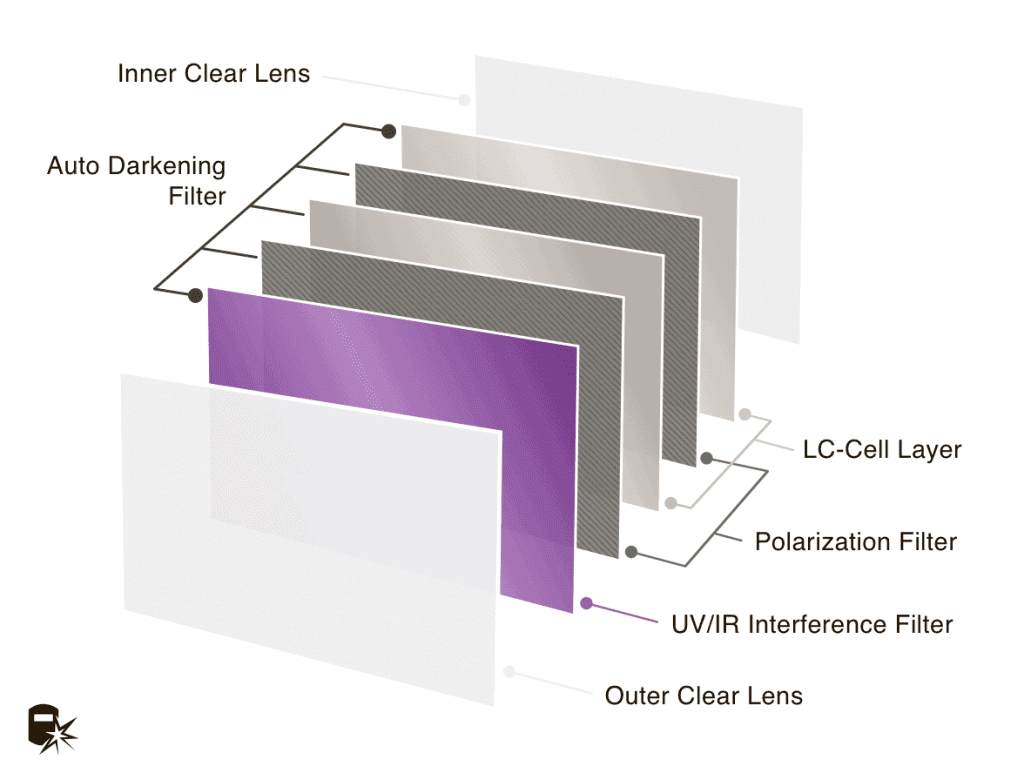
Optical Filters
Purpose of optical filters
Optical filters play a crucial role in solar-powered welding helmets by selectively allowing certain wavelengths of light to pass through while blocking others. The purpose of these filters is to protect welders’ eyes from harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation generated during welding while ensuring optimal visibility.
Types of optical filters used in welding helmets
Welding helmets utilize various types of optical filters to achieve the desired level of protection and visibility. One common filter used is a passive filter, which consists of colored glass that reduces the intensity of the light passing through. Another type is an active filter or liquid crystal display (LCD) filter, which can electronically adjust the darkness and transparency of the lens based on the welding arc’s brightness.
Filter specifications and classification
Optical filters used in solar-powered welding helmets are classified according to their shade numbers. The shade number refers to the level of darkness the filter provides, with higher numbers offering greater protection. The appropriate shade number depends on several factors, including the welding process, material being welded, and welding current. It is important to choose a helmet with the right shade number to ensure optimal eye protection and visibility.
Effect on visibility and color perception
While optical filters in welding helmets are designed to provide protection, they can also affect visibility and color perception. Welders may experience a reduction in overall brightness due to the darkened lens. Additionally, some optical filters may introduce a slight color shift, making it important for welders to consider these factors when selecting a helmet. However, advancements in filter technology have minimized these visibility and color perception issues, ensuring better clarity and color accuracy.
This image is property of Amazon.com.
Sensitivity and Delay Controls
Importance of sensitivity control
Sensitivity control is a vital feature in solar-powered welding helmets as it determines the helmet’s responsiveness to changes in light intensity. Welding environments can vary in terms of brightness, and the sensitivity control allows welders to adjust the helmet’s reaction to ensure optimal protection. By setting the sensitivity level to match the specific welding conditions, welders can prevent the lens from unnecessary darkening, allowing for a clearer view during low-intensity welding operations.
Adjustable delay settings for seamless transitions
Delay controls in solar-powered welding helmets enable welders to adjust the time it takes for the lens to transition from a darkened state back to a clear state after the welding arc has stopped. This feature ensures seamless transitions, preventing any sudden changes in lighting conditions that may cause discomfort or hinder visibility. Welders have the flexibility to set the delay time based on their personal preferences and welding techniques.
Impact on user comfort and safety
Sensitivity and delay controls significantly impact user comfort and safety while welding. With the ability to fine-tune the responsiveness and transition time of the helmet, welders can optimize their vision and adapt to different welding conditions. This customization enhances overall comfort, reduces eye strain, and increases the welder’s ability to accurately perform welding tasks with precision and confidence.
Power Source and Battery Life
Battery types used in solar-powered welding helmets
Solar-powered welding helmets incorporate various types of rechargeable batteries to store and supply power. Common battery types used include lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and lead-acid batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are widely favored for their high energy density, longer lifespan, and lighter weight. They provide a reliable power source for extended periods of welding, reducing the need for frequent recharging.
Charging mechanisms and alternatives
Solar-powered welding helmets are designed to be charged directly through their built-in solar panels, eliminating the need for external charging mechanisms. These helmets rely on exposure to sunlight, which is converted into electrical energy by the photovoltaic cells. In situations where sunlight is limited or not available, some helmets also offer alternative charging options such as USB charging or the use of additional external solar panels.
Battery life and performance considerations
The battery life of a solar-powered welding helmet depends on various factors, including the capacity of the battery, the power requirements of the helmet’s features, and how frequently those features are used. Manufacturers typically provide an estimated battery life based on average usage. It is important for welders to consider their welding demands and choose a helmet with a battery capacity that aligns with their requirements to ensure uninterrupted operation and minimize downtime.
This image is property of weldguru.com.
Design and Construction
Materials used in solar-powered welding helmets
Solar-powered welding helmets are constructed using durable and heat-resistant materials to withstand the harsh welding environment. The helmet’s shell is typically made of impact-resistant thermoplastic, providing protection against physical impacts from falling objects and welding debris. The lens, whether passive or active, is made from high-quality optical materials that offer excellent clarity and protection. Inner components and mechanisms are often designed using lightweight metals or engineering plastics to maintain a balanced and comfortable fit.
Ergonomic design features
Solar-powered welding helmets are designed with ergonomic features to enhance comfort and usability. Adjustable headbands and ratcheting systems allow welders to customize the fit of the helmet, ensuring a secure and stable position during welding. Padded interior linings and cushioning provide additional comfort, reducing pressure points and fatigue during long welding sessions. The overall design focuses on weight distribution and minimizing strain on the neck and shoulders, enabling welders to work for extended periods without discomfort.
Weight and balance considerations
Weight and balance are important factors to consider when selecting a solar-powered welding helmet. Welders often wear helmets for extended periods, and a heavy or poorly balanced helmet can cause fatigue and discomfort. Manufacturers strive to create lightweight helmets without compromising durability or safety. Through careful design and material selection, the weight is distributed evenly to minimize strain on the neck and ensure optimal balance during welding operations.
Durability and resistance to heat and sparks
Solar-powered welding helmets are subjected to high temperatures, intense light, and sparks generated during welding. To ensure durability and optimal protection, these helmets are constructed with materials that are heat-resistant and flame-retardant. The lens, in particular, must withstand intense light without warping or losing its optical properties. Additionally, the helmet’s outer shell is designed to withstand impacts from welding debris or other potential hazards, providing long-lasting protection in demanding welding environments.
Safety Features
Protection against ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation
Solar-powered welding helmets prioritize the safety of welders by offering protection against ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation generated during welding. The combination of optical filters and the helmet’s auto-darkening technology ensures that harmful UV and IR radiation is effectively blocked, preventing eye damage and long-term health risks associated with excessive exposure.
Heat and flame resistance
The materials used in solar-powered welding helmets are carefully selected to provide heat and flame resistance. The helmet’s shell and other components are designed to withstand high temperatures, sparks, and flames produced during welding. This ensures that the helmet remains intact and offers reliable protection even in the most intense welding conditions.
Dust and debris protection
Welding processes often generate a significant amount of welding debris, including sparks, slag, and metal particles. Solar-powered welding helmets incorporate design features that help protect the wearer’s face and eyes from these hazards. The helmet’s shape and coverage area, combined with a secure fit, create a barrier against airborne particles, reducing the risk of eye injuries and ensuring a safe and clean working environment.
Integration of respiratory protection
Some solar-powered welding helmets are designed to integrate with respiratory protection systems, offering an additional layer of safety. These helmets can be equipped with compatible respiratory devices such as powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) or supplied air systems. Integration of respiratory protection ensures that welders have adequate respiratory protection in environments where fumes or airborne contaminants are present.
This image is property of Amazon.com.
Maintenance and Care
Cleaning and storage recommendations
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of a solar-powered welding helmet, proper cleaning and storage practices are essential. Regularly cleaning the helmet’s shell, lens, and interior padding using mild soap and water can help remove dirt, dust, and welding residues. It is important to avoid using abrasive cleaners or solvents that may damage the helmet’s materials. When not in use, storing the helmet in a cool and dry place, preferably in a protective case or bag, helps prevent damage from environmental factors.
Shield replacement and adjustment
Over time, the lens or shield of a welding helmet may become scratched or damaged, compromising visibility and protection. Most solar-powered welding helmets allow for shield replacement, allowing welders to easily replace the lens when necessary. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for shield replacement to ensure proper fit and functionality. Additionally, periodic adjustments to the helmet’s headbands and straps may be required to maintain a comfortable and secure fit.
Inspecting and maintaining the solar power system
Solar-powered welding helmets rely on the functionality of the photovoltaic cells and associated electrical components. Regularly inspecting and maintaining the solar power system is essential to ensure reliable operation. Checking the condition of the solar panels and ensuring they are clean and free of obstructions allows for optimal sunlight absorption. Inspecting the wiring and connections for any signs of wear or damage helps prevent power interruptions. If any issues are identified, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer or a qualified professional for repairs or replacements.
Common troubleshooting tips
While solar-powered welding helmets are designed to be durable and reliable, occasional issues may arise. Some common troubleshooting tips include checking the battery charge level, verifying the integrity of the electrical connections, and ensuring the lens is clean and free of scratches. Adjusting sensitivity or delay settings may also help address issues related to lens responsiveness. It is important to consult the user manual or contact the manufacturer for specific troubleshooting guidance and support.
Choosing the Right Solar-powered Welding Helmet
Factors to consider when selecting a helmet
Choosing the right solar-powered welding helmet is crucial to ensuring adequate protection and optimal performance. Some important factors to consider include the helmet’s safety certifications, adjustable features, lens type and shade range, overall durability, and user comfort. It is also advised to evaluate the specific welding applications and requirements to determine the most suitable helmet for the job.
Budget and cost considerations
Solar-powered welding helmets come in a wide range of prices, and it is important to consider budget and cost when selecting a helmet. While higher-priced models often offer advanced features and greater durability, it is possible to find more affordable options that still meet safety and performance standards. It is recommended to analyze the specific needs and prioritize features that align with both the budget and desired level of protection.
User preferences and comfort
Every welder has unique preferences when it comes to helmet design and comfort. Evaluating factors such as helmet weight, headband adjustability, padding, and overall fit can help determine the level of comfort a particular helmet provides. Considering factors like ventilation, noise reduction, and visibility can further optimize the user experience. Ultimately, choosing a solar-powered welding helmet that offers a comfortable and customizable fit enhances work quality and reduces fatigue.
Certification and compliance standards
Solar-powered welding helmets must meet specific safety certifications and compliance standards to ensure quality and protection. It is crucial to choose helmets that comply with industry-recognized standards such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z87.1, which verifies impact resistance and optical clarity, and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60974-1, which ensures electrical and safety requirements for welding helmets. Checking for appropriate certification and compliance helps guarantee that the chosen helmet meets the necessary standards for reliable and effective eye and face protection.
In conclusion, solar-powered welding helmets offer numerous advantages over traditional helmets, making them increasingly popular among welders. Harnessing the power of solar energy, these helmets provide a continuous and convenient power supply without the need for frequent battery changes or recharging. With features such as auto-darkening technology, adjustable shade levels, and quick reaction times, solar-powered helmets enhance safety, visibility, and user comfort. The utilization of optical filters ensures eye protection from harmful radiation, while sensitivity and delay controls allow for customization and optimal performance. Considerations such as power source, construction, safety features, and maintenance are crucial when selecting a solar-powered welding helmet. By understanding the technology and carefully evaluating the specific requirements, welders can choose a helmet that meets their needs, enhances safety, and provides a comfortable and efficient welding experience.
This image is property of waterwelders.com.