When it comes to joining materials together, welding is an essential skill widely used in industries and various construction projects. From creating sturdy structures to repairing broken parts, welding plays a vital role in building and maintaining our world. In this article, we explore the fascinating realm of welding processes, examining the diverse techniques that welders employ to connect metal pieces and bring their creative visions to life. So, whether you’ve always been curious about the art of welding or are simply looking to expand your knowledge, join us as we embark on an exciting exploration of the different types of welding processes.
Review contents
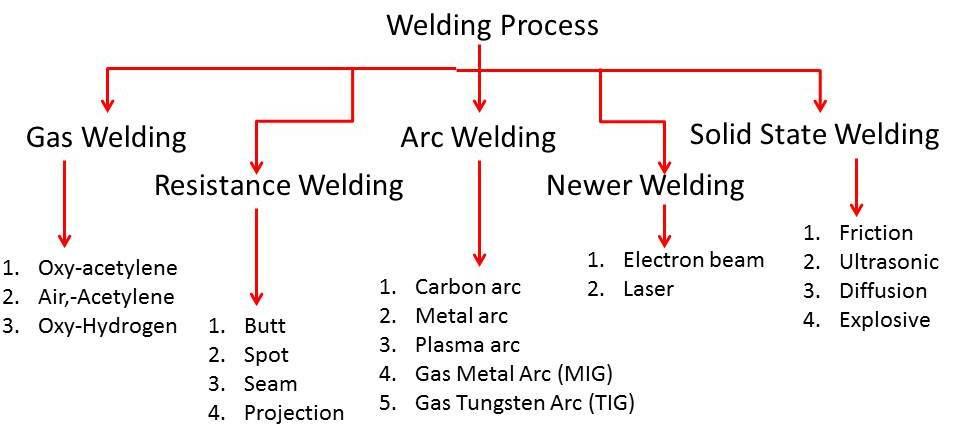
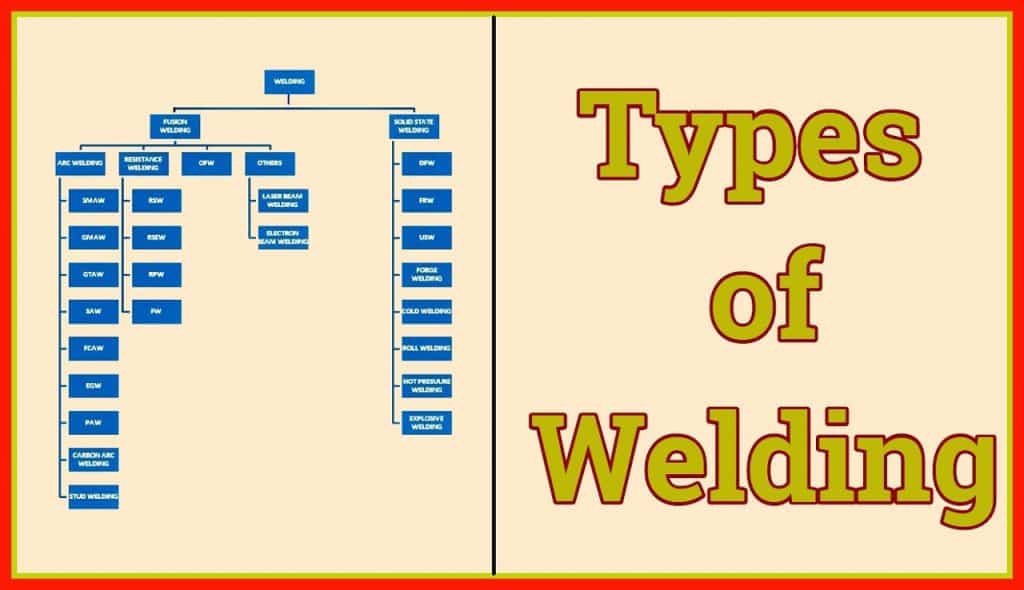
Arc Welding
Arc welding is a versatile and widely used welding process that utilizes an electric arc to join metal pieces together. This process relies on the intense heat generated by the electrical discharge between the welding electrode and the metal workpiece. There are several different techniques of arc welding, each suited for specific applications. In this article, we will explore some of the most common types of arc welding.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
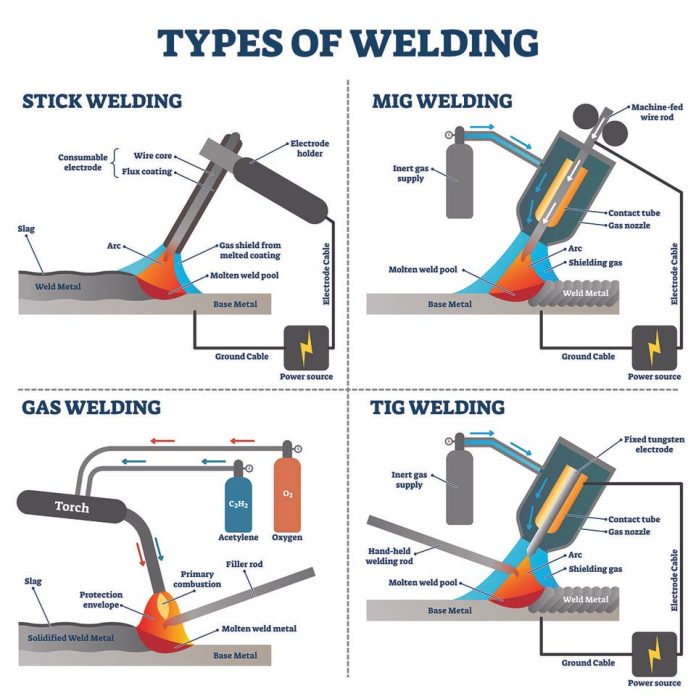
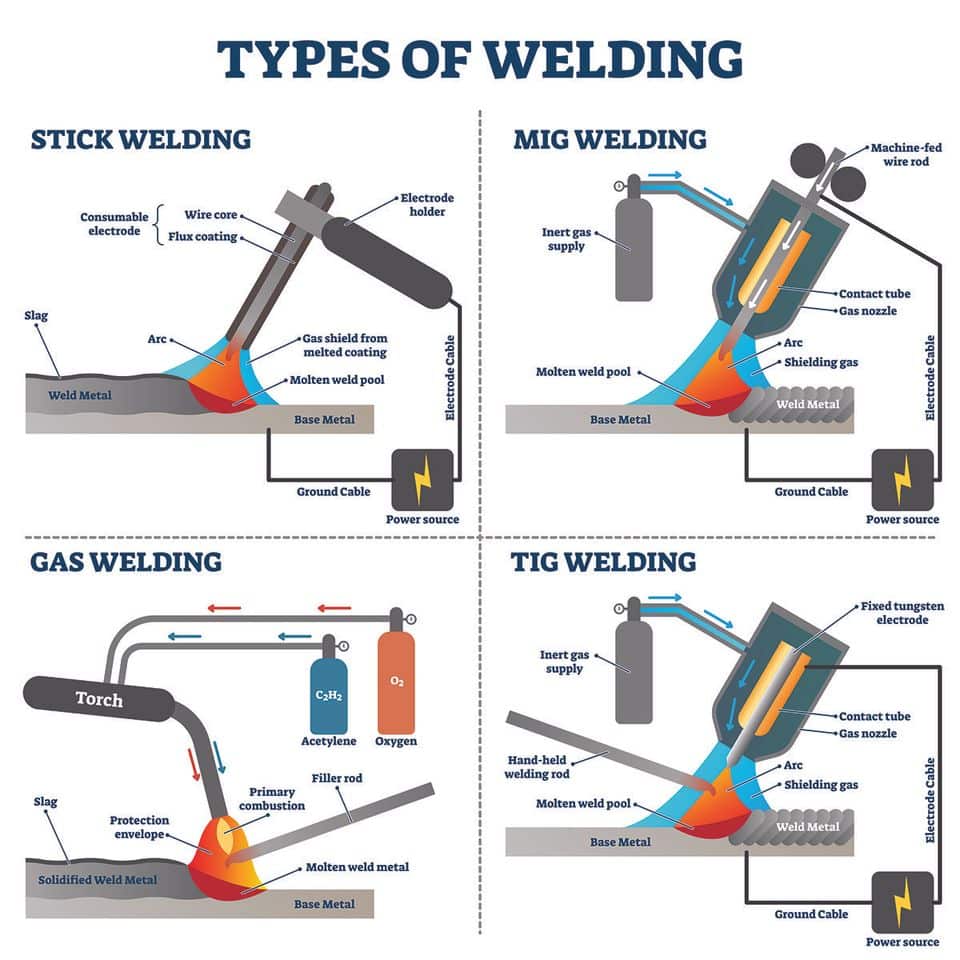
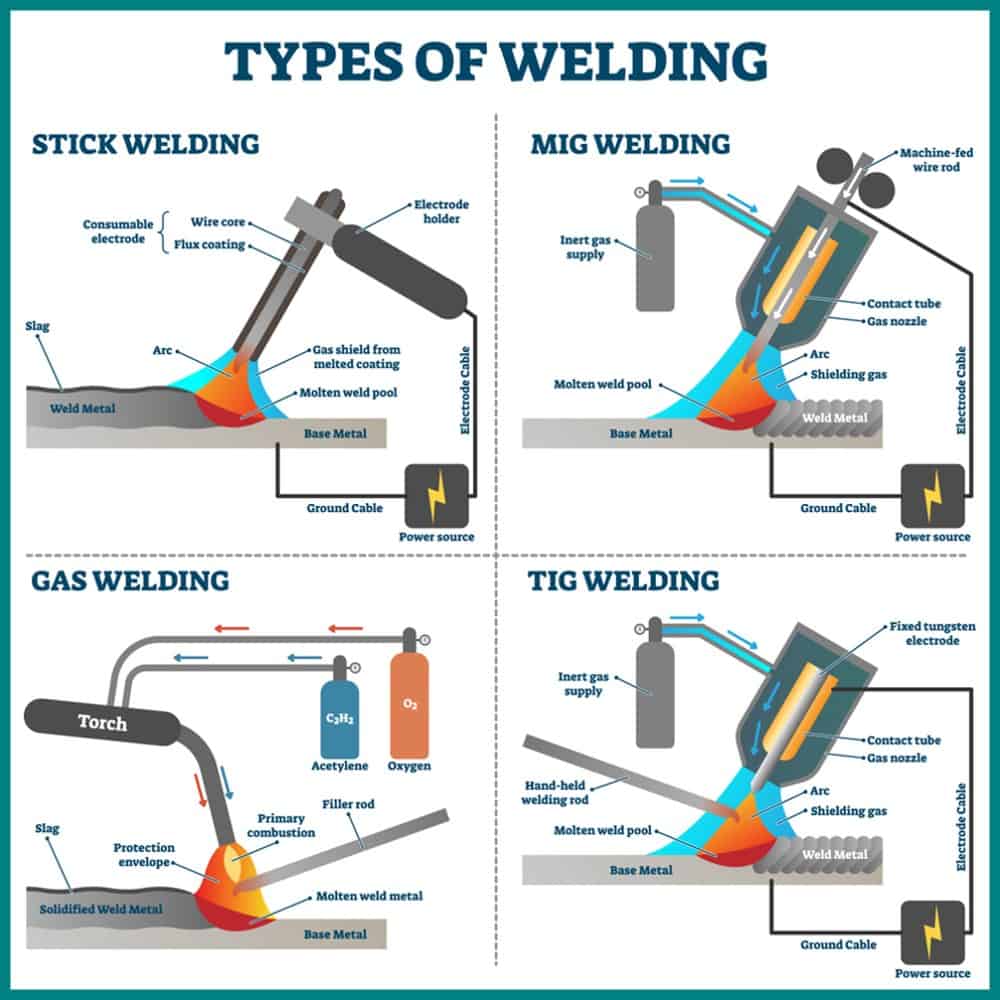
Shielded Metal Arc Welding, also known as stick welding, is one of the oldest and most reliable arc welding processes. It uses a consumable electrode coated in flux, which provides shielding gas and creates a slag to protect the weld pool. SMAW is commonly used for welding thick materials, on-site repairs, and in industries such as construction and automotive.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Gas Metal Arc Welding, or MIG welding, is a popular arc welding process that uses a continuous solid wire electrode and a shielding gas to protect the weld pool. GMAW offers high productivity and is suitable for both thin and thick materials. It is widely used in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and fabrication.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Flux-Cored Arc Welding is a variation of GMAW that uses a tubular flux-cored wire instead of a solid wire electrode. The flux within the wire provides shielding gas and produces slag, eliminating the need for an external shielding gas. FCAW is commonly used in heavy fabrication, shipbuilding, and construction industries.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, commonly known as TIG welding, is a precise and versatile arc welding process. It uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas, typically argon, for shielding. TIG welding produces high-quality, clean welds and is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and artistic fabrication.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Submerged Arc Welding is an arc welding process that utilizes a continuously fed consumable electrode and a granular flux to create a protective blanket over the weld pool. SAW is commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as welding thick plates, pipes, and pressure vessels. It provides high welding speeds and exceptional weld quality.
Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a group of welding processes that create welds by applying pressure and passing current through the joint. These processes are efficient and widely used in a variety of industries. Let’s explore some of the common types of resistance welding.
Spot Welding
Spot welding is a resistance welding process primarily used for joining two overlapping metal sheets together. It involves the application of electrode pressure onto the metal sheets, followed by passing a high electric current through the joint. Spot welding is commonly used in automotive manufacturing, appliance production, and sheet metal fabrication.
Seam Welding
Seam welding is similar to spot welding but is used for creating long continuous welds along the length of overlapping metal sheets or tubes. The electrodes in seam welding continuously glide over the joint, creating a series of overlapping spot welds. Seam welding is widely used in the production of fuel tanks, pipelines, and automotive components.
Projection Welding
Projection welding is a resistance welding process that is used to join metal parts with small projections or embossed features. These projections concentrate the heat and pressure, ensuring a strong and reliable weld. Projection welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, HVAC, and electrical appliance manufacturing.
Flash Welding
Flash welding is a resistance welding process that involves the use of intense heat generated by an electrical discharge. The heat creates a molten state within the joint, and the applied pressure fuses the metals together. Flash welding is commonly used for joining large components, such as rails, rods, and shafts.
This image is property of lirp.cdn-website.com.
Gas Welding
Gas welding processes utilize a flame generated by burning a fuel gas mixed with oxygen to melt and join metal surfaces. While these processes are not as commonly used as arc welding or resistance welding, they still have their applications in specific industries. Let’s explore two common types of gas welding.
Oxyfuel Gas Welding
Oxyfuel Gas Welding, also known as oxyacetylene welding, is a gas welding process that uses a mixture of fuel gas, typically acetylene, and oxygen to create a flame. The heat from the flame melts the metal surfaces, and a filler rod can be added to create the weld joint. Oxyfuel gas welding is versatile and can be used for various metals, making it popular in jewelry making, plumbing repairs, and artistic fabrication.
Air Acetylene Welding
Air Acetylene Welding is a gas welding process that uses a mixture of acetylene and air to create a flame. This process provides a slightly cooler flame compared to oxyfuel gas welding, making it suitable for more delicate materials. Air acetylene welding is often used for soldering, jewelry repair, and small-scale brazing.
Energy Beam Welding
Energy beam welding processes use high-energy beams, such as laser or electron beams, to melt and join metal parts together. These processes offer precise control and produce high-quality welds. Let’s explore two types of energy beam welding.
Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
Laser Beam Welding is an energy beam welding process that utilizes a focused laser beam to heat the metal surfaces and create a weld joint. The high energy density of the laser beam allows for precise control and minimal heat-affected zones. Laser beam welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Electron Beam Welding (EBW)
Electron Beam Welding is an energy beam welding process that uses a highly focused electron beam to melt and join metal parts. The electron beam is generated in a vacuum, allowing for precise control and deep penetration. Electron beam welding is commonly used in aerospace, nuclear, and automotive industries, where high-quality and reliable welds are crucial.
This image is property of mechanical-engineering.s3.amazonaws.com.
Solid-state Welding
Solid-state welding processes create welds without fully melting the metal surfaces. These processes are suitable for joining different materials and producing strong welds. Let’s explore some common types of solid-state welding.
Friction Welding
Friction Welding is a solid-state welding process that uses the heat generated by friction between two parts to forge them together. The parts are pressed together and rotated, generating heat that softens the materials. When enough heat is generated, the rotating motion stops, and the parts are forged together under pressure. Friction welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and power generation.
Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic Welding is a solid-state welding process that uses high-frequency mechanical vibrations to create heat and weld two parts together. The parts are held together under pressure while ultrasonic vibrations are applied, causing the material to soften and fuse. Ultrasonic welding is commonly used in the electronics, medical device, and automotive industries.
Explosion Welding
Explosion Welding is a solid-state welding process that joins metal plates together using controlled explosive forces. The impact from the explosion creates a high-pressure wave that allows the atoms of the two metals to merge together. Explosion welding is commonly used for joining dissimilar metals and in industries such as shipbuilding, oil and gas, and nuclear power.
Thermite Welding
Thermite Welding is a welding process that uses a chemical reaction between metallic powders to generate intense heat for welding. A mixture of aluminum powder and metal oxide is ignited, resulting in a thermite reaction that releases a vast amount of heat. This process is commonly used for joining railroad tracks, electrical connections, and other large-scale applications.
This image is property of www.cruxweld.com.
Induction Welding
Induction Welding is a process that uses electromagnetic induction to create heat and join two or more metal parts together. The parts are placed within an induction coil, and an alternating current is passed through the coil, generating an oscillating magnetic field. This field induces eddy currents in the metal parts, creating localized heat that fuses the parts. Induction welding is commonly used in the automotive, aerospace, and HVAC industries.
Electroslag Welding
Electroslag Welding is a welding process that uses the heat generated by an electric current passing through a slag pool to melt the metal parts together. The slag acts as a resistive element, allowing the electric current to pass and generating heat. Electroslag welding is commonly used for joining thick sections of metal, such as bridge girders, ship hulls, and heavy machinery parts.
This image is property of www.steelfabricatorssydney.com.au.
Forge Welding
Forge Welding is an ancient welding process that involves heating metal parts to a high temperature and hammering them together to create a weld. The heat softens the metal surfaces, and the hammering action forges them together. Forge welding is commonly used in blacksmithing, artistic fabrication, and traditional metalworking.
Plasma Arc Welding
Plasma Arc Welding is an arc welding process that employs a highly ionized gas, or plasma, to create a high-temperature arc and melt metal surfaces. The plasma is formed by passing a gas through a narrow orifice and applying a high-frequency electrical current. Plasma arc welding is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor industries for its precise control and high-quality welds.
In conclusion, there are various types of welding processes available, each suited for different applications and materials. From the versatile and reliable arc welding techniques to the efficient resistance welding methods, and the precise energy beam and solid-state welding processes, there is a welding method for every need. Whether it’s joining metal sheets, creating long continuous welds, or even welding without fully melting the metal surfaces, these processes enable us to bring together different components and create strong, durable connections.
This image is property of www.weldingandndt.com.